
Our experience demonstrated that this surgical technique reduced the intraoperative risk for patients. After that, the rod of nail was pulled back a little to make the wire in the middle of the tack hole, which can facilitate the insertion of the PFNA blade or lag screw. Through this way, the lag screw and helical blade get a good purchase that docked at femoral calcar. Therefore, the superior border of the tack hole can be used as presser to prevent the wire from deviating upward. When guide wire just passed the tack hole of the nail, the rod of nail was slightly tapped down further to allow the superior border of the tack hole to touch the guide wire. Here, we are presenting a surgical technique to direct the guide wire to right track. The guide wire would always bend and flow superiorly away from femoral calcar, and the lag screw and helical blade will follow the track and get into superior part of femoral head, not into femoral calcar. Inclusion criteria were intertrochanteric femur fracture with long intramedullary nail (IMN) fixation and age equal to or older than 18 years. One of difficulties encountered in operation is insertion of the guide wire to femoral head. The involved patients were collected from the clinic’s database based on a computer query of Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes for trochanteric fractures.
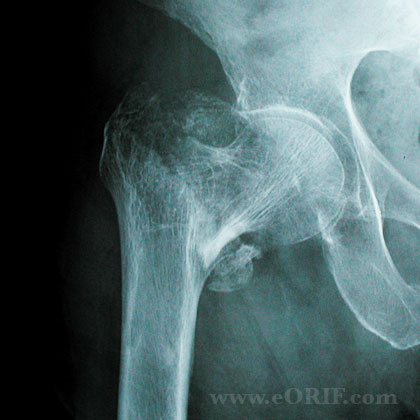
Cephalomedullary fixation, including proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) and gamma nail, is commonly used in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. Intertrochanteric fracture is the most common hip fractures in elderly population.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
